Copy number variation alters local and global mutational tolerance.
Grace Avecilla, Pieter Spealman, Julia Matthews, Elodie Caudal, Joseph Schacherer, David Gresham.
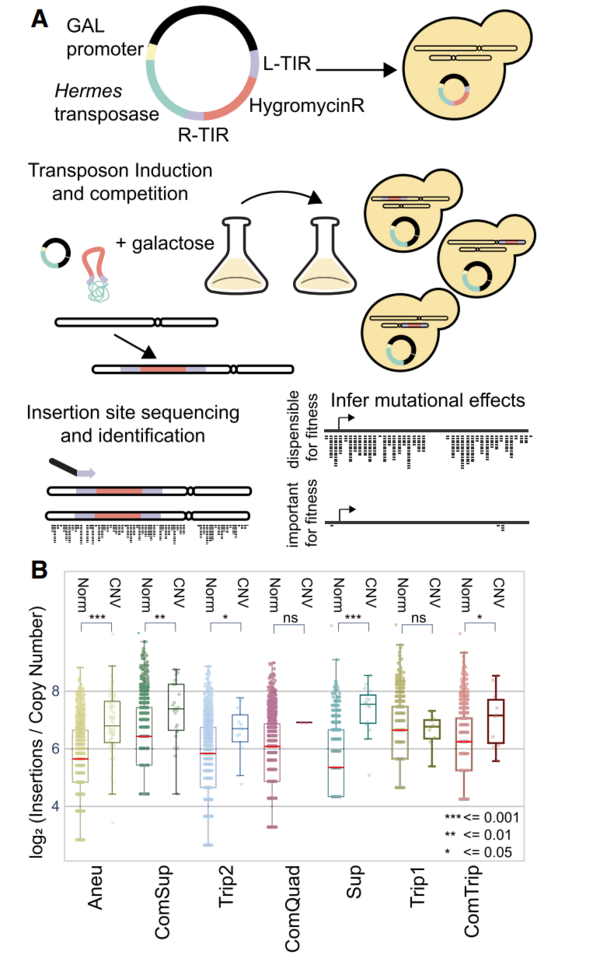
Copy number variants (CNVs), duplications and deletions of genomic sequences, contribute to evolutionary adaptation but can also confer deleterious effects and cause disease. Whereas the effects of amplifying individual genes or whole chromosomes (i.e., aneuploidy) have been studied extensively, much less is known about the genetic and functional effects of CNVs of differing sizes and structures. Here, we investigated Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) strains that acquired adaptive CNVs of variable structures and copy numbers following experimental evolution in glutamine-limited chemostats. Although beneficial in the selective environment, CNVs result in decreased fitness compared with the euploid ancestor in rich media. We used transposon mutagenesis to investigate mutational tolerance and genome-wide genetic interactions in CNV strains. We find that CNVs increase mutational target size, confer increased mutational tolerance in amplified essential genes, and result in novel genetic interactions with unlinked genes. We validated a novel genetic interaction between different CNVs and BMH1 that was common to multiple strains. We also analyzed global gene expression and found that transcriptional dosage compensation does not affect most genes amplified by CNVs, although gene-specific transcriptional dosage compensation does occur for ∼12% of amplified genes. Furthermore, we find that CNV strains do not show previously described transcriptional signatures of aneuploidy. Our study reveals the extent to which local and global mutational tolerance is modified by CNVs with implications for genome evolution and CNV-associated diseases, such as cancer.